210 2231624
Shaft Alignment System
-
Top Seller
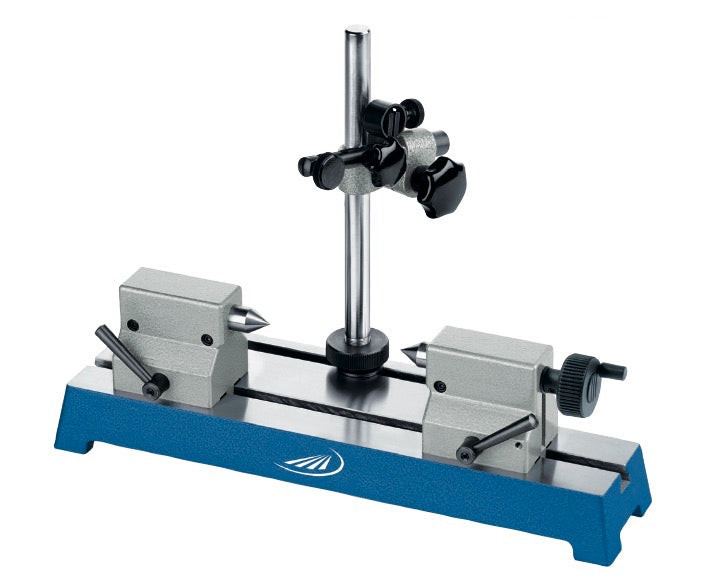
 668-SET
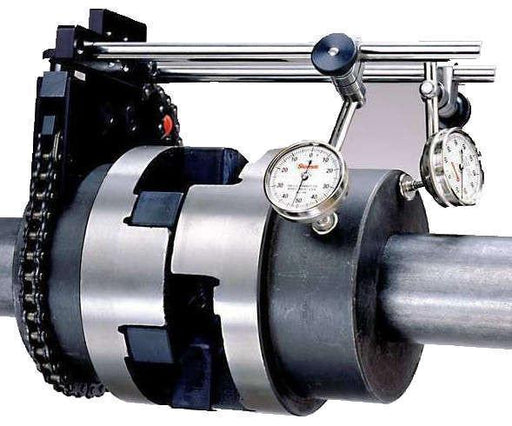
668-SET668 - Shaft Alignment Clamp Sets
Original price €945,00 - Original price €945,00Original price€945,00€945,00 - €945,00Current price €945,00| /Includes: (A) 668 Chain Clamp Only (EDP 667155 ) PCS 1 (B) PT99529 Ext plate screw washer (EDP 67454) PCS 1 (D) 657G Upright base p...
View full detailsΔιαθέσιμο
Σχετικές Κατηγορίες
A mechanical shaft alignment system and a laser shaft alignment system are both tools used to align two shafts in rotating machinery. They serve the same purpose of ensuring precise alignment between the two shafts to prevent issues such as excessive vibrations, premature wear, and increased energy consumption. However, they differ in terms of their technology and the alignment process.
Mechanical Shaft Alignment System:
A mechanical shaft alignment system typically includes tools like straightedges, dial indicators, and feeler gauges. The process involves the use of these manual instruments to measure and correct misalignment between the shafts. Here's how it generally works:
Mounting the tools: The straightedges and dial indicators are attached to the shafts using magnetic bases or brackets. The straightedge is used to create a reference line along the shafts' length, while the dial indicators measure any shaft misalignment relative to this reference line.
Taking measurements: As the shafts are rotated, the dial indicators provide readings that indicate the misalignment in terms of offset and angularity. The alignment technician interprets these readings to understand the adjustment required.
Making adjustments: Based on the measurements, adjustments are made to the position of one or both shafts until the misalignment is minimized or eliminated. This process is iterative, requiring multiple measurements and adjustments until the desired alignment is achieved.
Laser Shaft Alignment System:
A laser shaft alignment system employs advanced laser technology for more accurate and efficient alignment. It includes a laser alignment device, typically equipped with laser transmitters and detectors, and special fixtures (often called targets or sensors) that attach to the shafts. Here's how it generally works:
Mounting the fixtures: The laser targets are attached to each shaft, typically using chain brackets or magnetic bases. The laser alignment device is mounted on one of the shafts and emits a laser beam towards the other shaft.
Laser alignment: The laser beam establishes a straight reference line along the shafts' rotational axes. The laser detectors on the opposite shaft receive the laser beam.
Taking measurements: As the shafts are rotated, the laser detectors measure any misalignment between the shafts by detecting the laser beam's movement relative to the reference line.
Making adjustments: The alignment technician adjusts the position of one or both shafts until the laser beam remains centered on the detector throughout the rotation, indicating proper alignment. Like the mechanical system, this process may require multiple iterations for precise alignment.
Laser shaft alignment systems generally provide more accurate and quicker results compared to mechanical systems. They are widely used in various industries due to their efficiency, ease of use, and ability to measure and correct misalignments with high precision